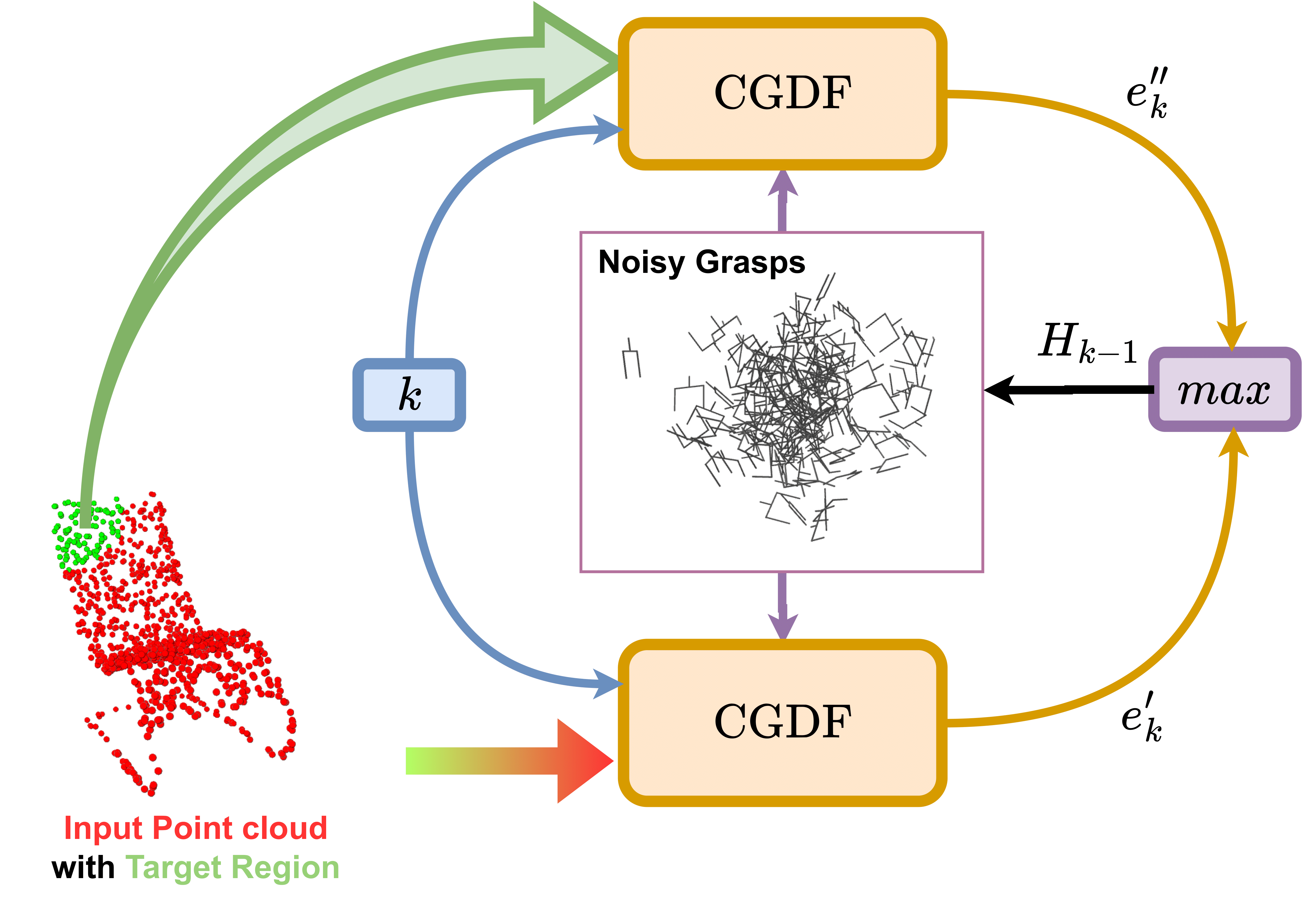
Architecture
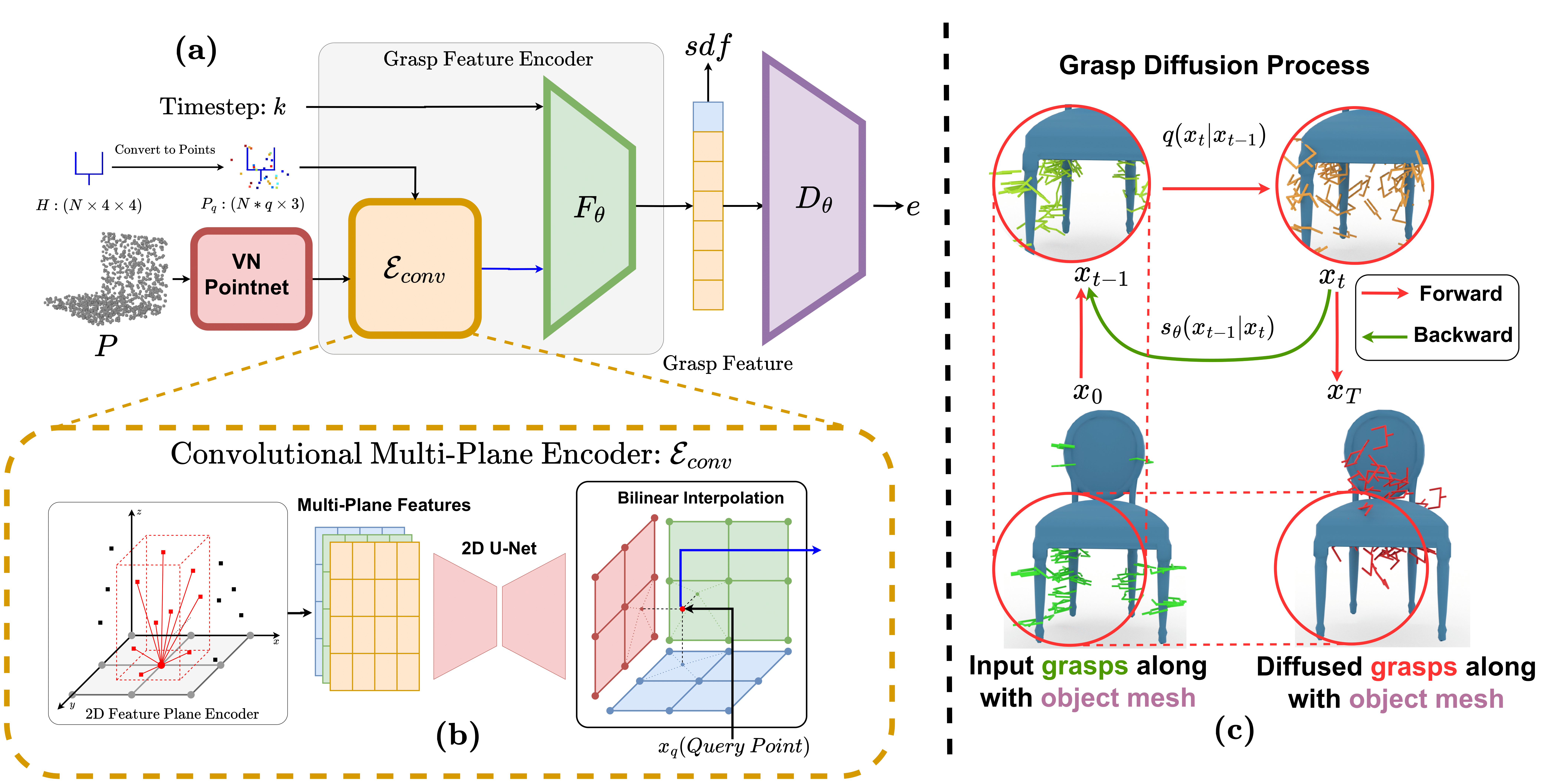
Architectural Overview:The figure section (a) shows the architecture of our
proposed energy-based model \(\mathbf{E_{\theta}} \).
During this process, the model takes as input a point cloud and the grasp pose, which is
subsequently converted into a set of query points.
We use a VN-Pointnet-based point cloud encoder, which generates per-point features. (b)
shows how these features are then distilled into
three 2D feature planes oriented along the \(XY\), \(XZ\), and \(YZ\) planes using a
convolutional
multi-plane encoder. For each grasp pose, feature
vectors corresponding to \(N\) query points are obtained using bilinear interpolation on the
feature planes. Subsequently, the grasp feature
vector is derived from \(\mathbf{F_{\theta}} \) and decoded into an energy value by
\(\mathbf{D_{\theta}} \) . In figure section
(c), we show the grasp diffusion process, where
grasps are diffused over the object during the forward diffusion process and denoised
using the backward diffusion process.